
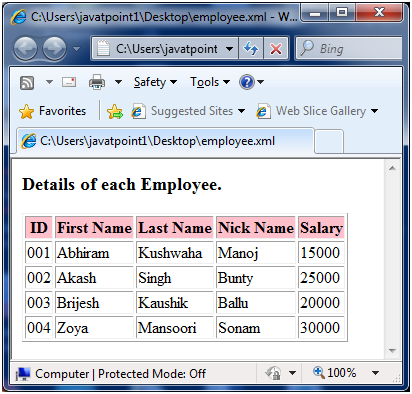
In this example, we've created a sample XML document students.xml and its stylesheet document students.xsl which uses the XPath expressions.įollowing is the sample XML used. If location path starts with the node that we've selected then it is a relative path.įollowing are few examples locating the elements using relative path.įirstname − select firstname related to student nodes.
You must escape these characters using XML &-encoding, or specify the XPath in the URL.Location path specifies the location of node in XML document.

Specifying Boolean Operators in XPath Queries (SQLXML 4.0) Specifying Explicit Conversion Functions in XPath Queries (SQLXML 4.0) Specifying Relational Operators in XPath Queries (SQLXML 4.0) Specifying Arithmetic Operators in XPath Queries (SQLXML 4.0) Specifying Axes in XPath Queries (SQLXML 4.0)īoolean-valued predicates including successive and nested predicates The following table shows the features of the XPath language that are implemented in SQLXML 4.0. The tables in the following sections provide details about how the implementation of XPath queries in SQLXML 4.0 differs from the W3C specification in these areas. However, SQLXML 4.0 does support queries such as which selects Customers with any Order for which the OrderDate equals its ShipDate.ĭepending on the schema and XPath query expression that are used, Transact-SQL errors could be exposed to users under certain conditions. SQLXML 4.0 does not support cross-product XPath queries, such as This query selects all Customers with any Order for which the OrderDate equals the ShipDate of any Order. For more information, see XPath Data Types (SQLXML 4.0). SQLXML 4.0 has limitations in implementing the XPath string, number, and boolean data types. However, this is not the primary use of these annotations For more information, see Identifying Key Columns Using sql:key-fields (SQLXML 4.0) and Specifying Relationships Using sql:relationship (SQLXML 4.0). In some cases, the key-fields annotation or keys from the relationship annotation can result in a deterministic document order.

An element with child elements or an IDREFS or NMTOKENS node cannot be converted to string. The lack of document order also means that the string value of a node can be evaluated only when that node maps to a single column in a single row. Therefore, numeric predicates and axes that use document order (such as following) are not implemented. In SQLXML 4.0, document order is not always determined. In SQLXML 4.0, a query can return many types of error messages. XPath queries that fail to select any nodes return an empty node-set. The W3C XPath specification defines no error conditions. I include my own time in the calculation of 'efficiency' - I'll take any existing solution for this problem. which would return the relative path from node1 to node2. Every XPath query must begin at a top-level in the schema. Essentially the interface would look something like: my xpath getpath (node1, node2). SQLXML 4.0 does not support the root query (/).
The following are key differences between the W3C XPath implementation and the SQLXML 4.0 implementation. SQLXML 4.0 implements a subset of the W3C XPath specification, which is located at. The XPath language is defined by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) as a standard navigation language. The resulting node-set contains all the orders with order date. For example, given a set of nodes, XPath can select all nodes with the date attribute value of "". Each XPath operator selects a node-set based on a node-set selected by a previous XPath operator. XPath is a graph navigation language used to select a set of nodes from an XML document. In this document, is an element node, cid is an attribute node, and "Important" is a text node. For example, consider this XML document: For more information, see Introduction to Annotated XSD Schemas (SQLXML 4.0), and the XPath standard defined by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C).Īn XML document consists of nodes such as an element node, attribute node, text node, and so on. To understand XPath queries in SQLXML 4.0, you must be familiar with XML views and related concepts such as templates and mapping schema.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
